Intel Launches 12th Gen Core Desktop Alder Lake Processors

Today Intel is launching the first products in their 12th Gen Core family, their top-end high-performance desktop processors. Intel’s 12th generation Core processors are based on the heterogeneous multi-core Alder Lake microarchitecture which we will revisit in more detail later in this article. In total, the full 12th Gen Core family will incorporate 60 processors and power over 500 designs with 28 of them already shipping to partners. Today, however, the company is launching the first six – high-performance, high-power desktop processors for gamers, enthusiasts, and professional creators.
Initial Lineup
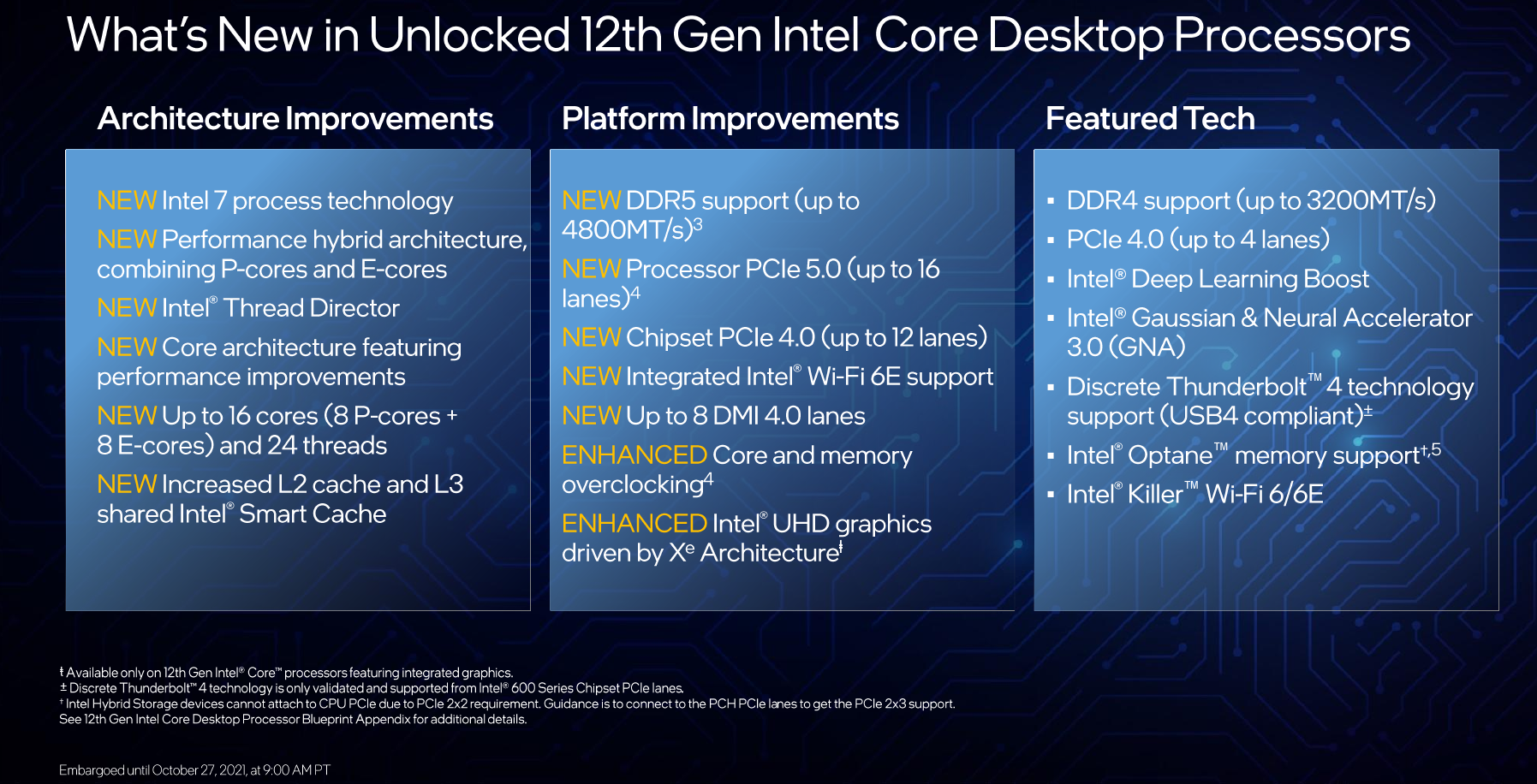
Six new desktop processors are announced today. All of them are unlocked overclockable K SKUs with already-high turbo frequencies in excess of 4.9 GHz. The ability to overclock includes the performance as well as the efficiency cores and both DDR4/DDR5 memory (along with XMP 3.0). Half of the SKUs (K) come with integrated graphics while the other half (KF SKUs) come without. All six processors bring 20 lanes of PCIe – x16 lanes supporting PCIe 5.0 with x4 more lanes of PCIe 4.0. Additionally, all six processors support up to 128 GiB of DDR5 supporting data rates of up to 4800 MT/s. Because Alder Lake is a heterogeneous multi-core design, the SKUs come in a varying number of performance (P) and efficiency (E) cores.
12th Generation Core processors are shipping today to partners.
| 12th Gen Core i Processors | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | Cores | L3 | L2 | Base | Turbo | Power | Price | ||||
| P-core | E-core | TBMT | P-core | E-core | Base | Max Turbo | |||||
| i5-12600KF | 10C/16T (6P+4E) |
20 MiB | 9.5 MiB | 3.7 | 2.8 | — | Up to 4.9 | Up to 3.6 | 125 W | 150 W | $264 |
| i5-12600K | 10C/16T (6P+4E) |
20 MiB | 9.5 MiB | 3.7 | 2.8 | — | Up to 4.9 | Up to 3.6 | 125 W | 150 W | $289 |
| i7-12700KF | 12C/20T (8P+4E) |
25 MiB | 12 MiB | 3.6 | 2.7 | Up to 5.0 | Up to 4.9 | Up to 3.8 | 125 W | 190 W | $384 |
| i7-12700K | 12C/20T (8P+4E) |
25 MiB | 12 MiB | 3.6 | 2.7 | Up to 5.0 | Up to 4.9 | Up to 3.8 | 125 W | 190 W | $409 |
| i9-12900KF | 16C/24T (8P+8E) |
30 MiB | 14 MiB | 3.2 | 2.4 | Up to 5.2 | Up to 5.1 | Up to 3.9 | 125 W | 241 W | $564 |
| i9-12900K | 16C/24T (8P+8E) |
30 MiB | 14 MiB | 3.2 | 2.4 | Up to 5.2 | Up to 5.1 | Up to 3.9 | 125 W | 241 W | $589 |
Alder Lake
The complete Alder Lake microarchitecture will feature 60 processors that will cover the entire compute spectrum from ultra-low-power mobile devices to high-performance desktops. For the desktop segment which includes all of today’s processors, Alder Lake utilizes the LGA-1700 socket which is a 2-chip platform – the processor and the chipset. Future mobile and ultra-mobile processors will utilize the BGA Type3 and BGA Type4 HDI packages.
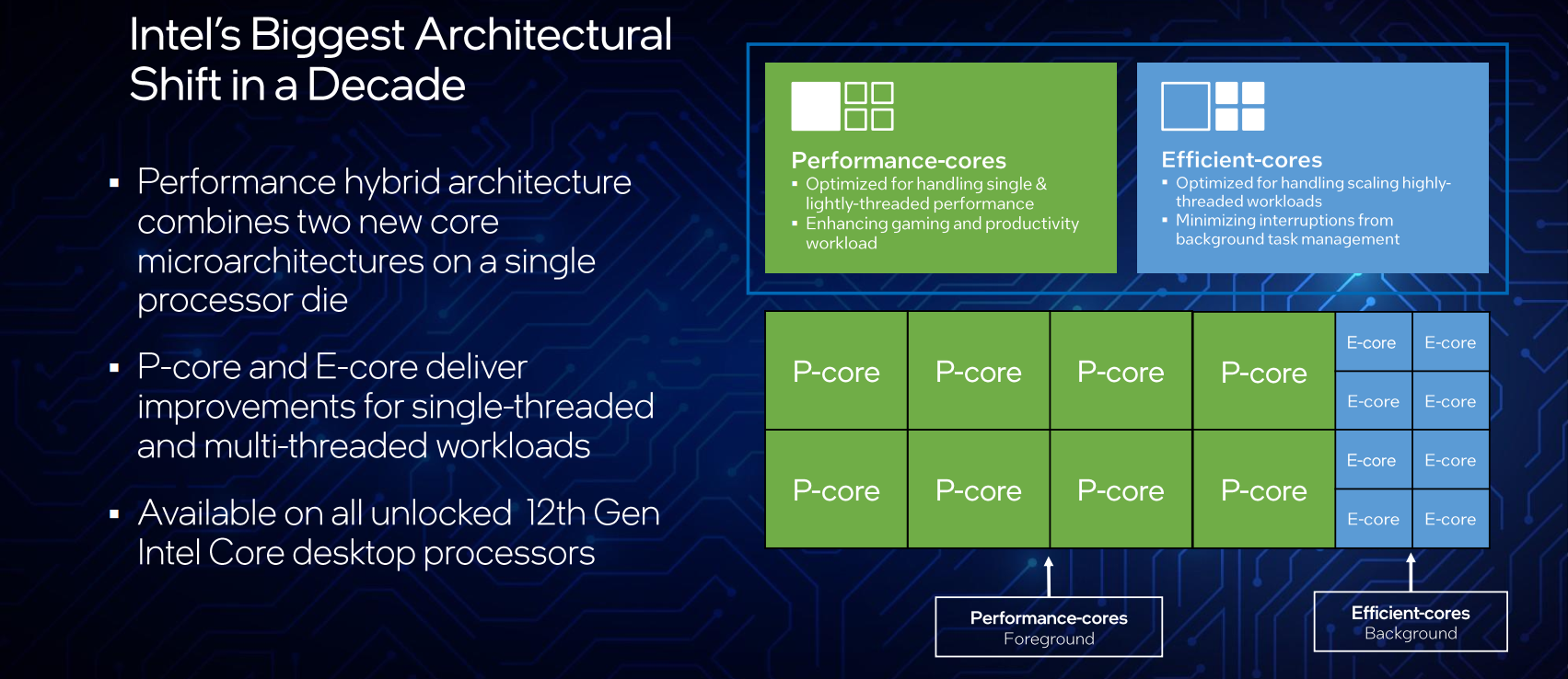
As we detailed back in August, Alder Lake integrates up to eight high-performance cores along with up to eight high-efficiency cores. Intel refers to those cores as P-core and E-core respectively, a nomenclature originally introduced by Apple for the same purpose. The performance cores are based on the big Golden Cove microarchitecture while the efficiency cores are based on the Gracemont microarchitecture.
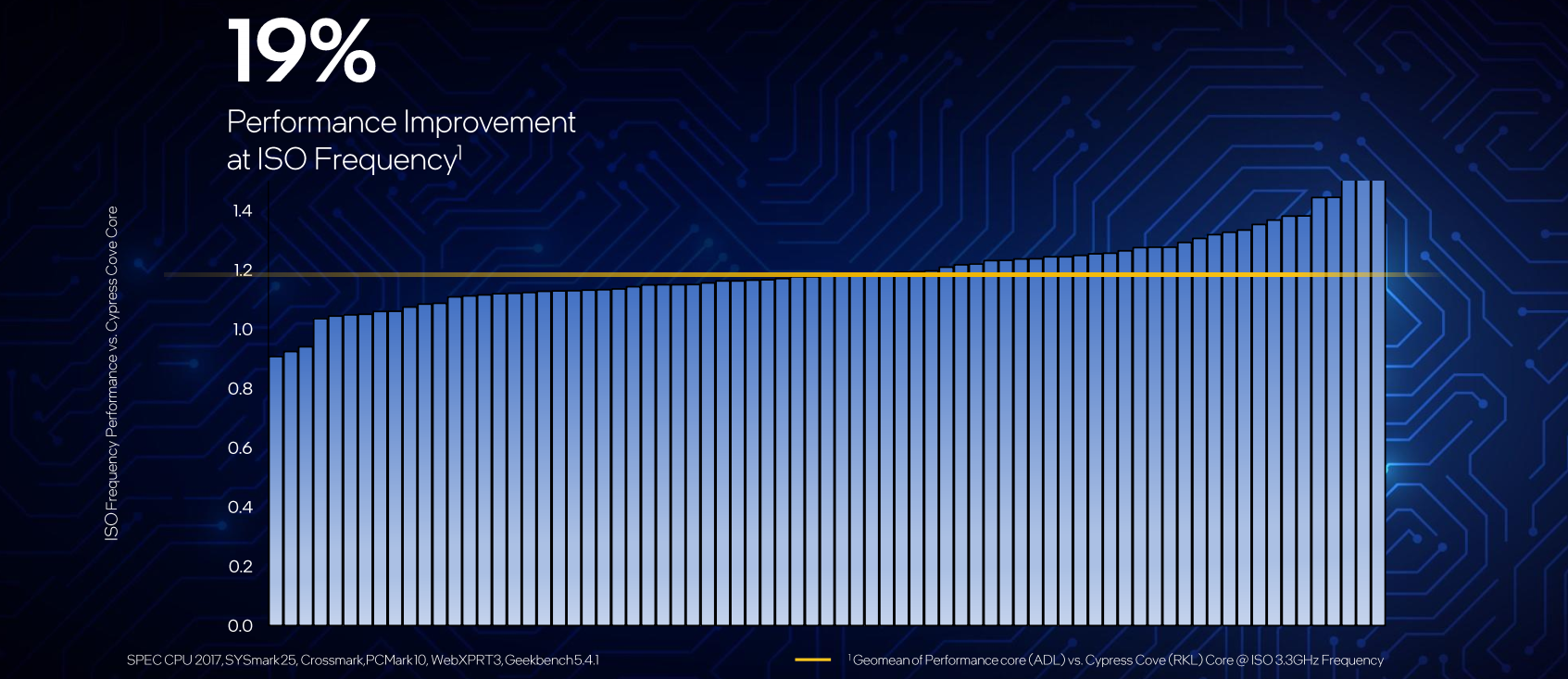
Compared to prior, Willow Cove, Golden Cove is said to deliver a 19% improvement in IPC. But perhaps even more impressive, the Gracement high-efficiency Gracemont cores are said to deliver 40% higher Performace at iso-power versus Skylake or, alternatively, achieving the same performance while consuming less than 40% of the power. For the new K unlocked SKUs, both the P-cores and E-cores are overclockable.
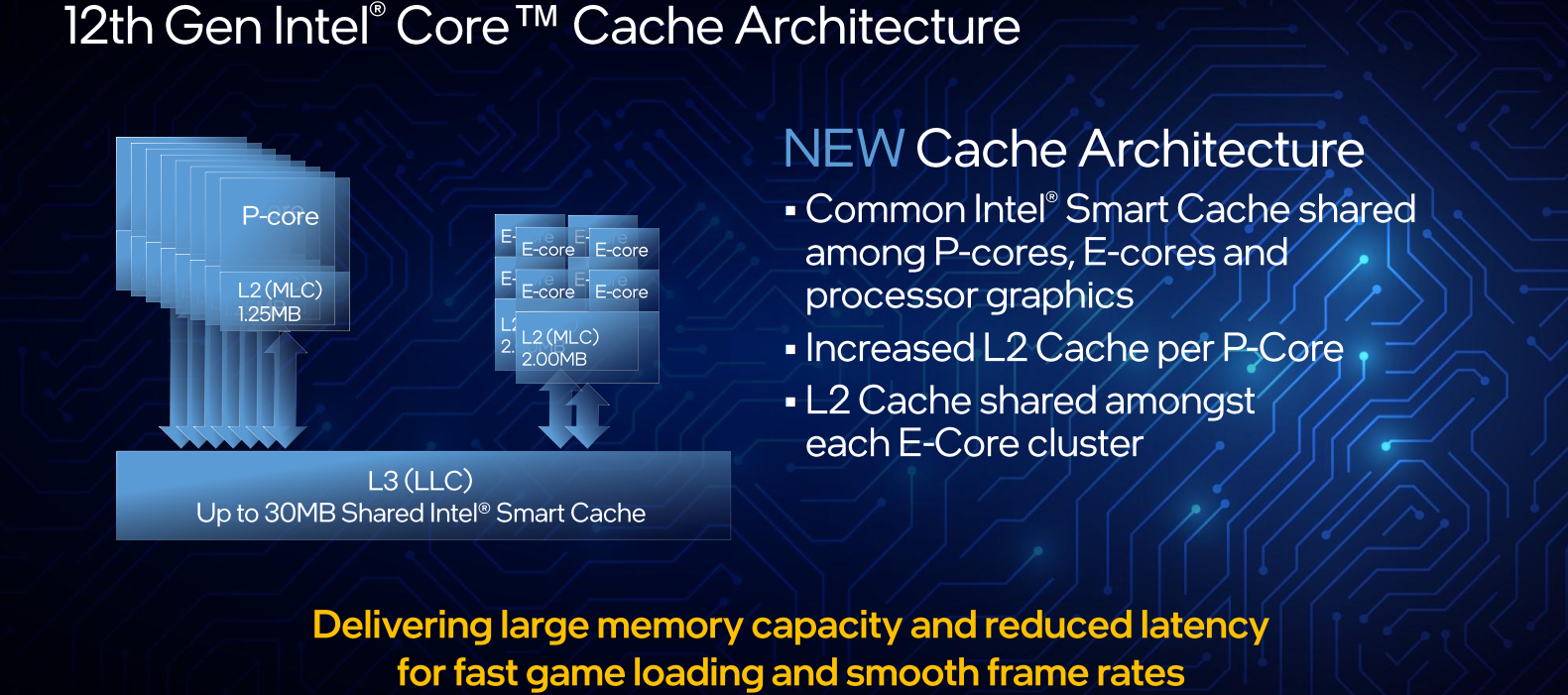
With the integration of both big cores and small cores on a single SoC, the cache architecture is slightly different. On Alder Lake, each P-core is more or less an independent component featuring its own private L2 cache with a total capacity of 1.25 MiB. Eight instances of that are integrated onto a single SoC. The E-cores, on the other hand, are bundled into a quad-core cluster with 2 MiB of L2 cache shared amongst them. Two instances of the E-core cluster are integrated onto a single SoC. Across the entire chip, up to 30 MiB of LLC is shared by the P-cores, E-cores cluster, and integrated graphics.
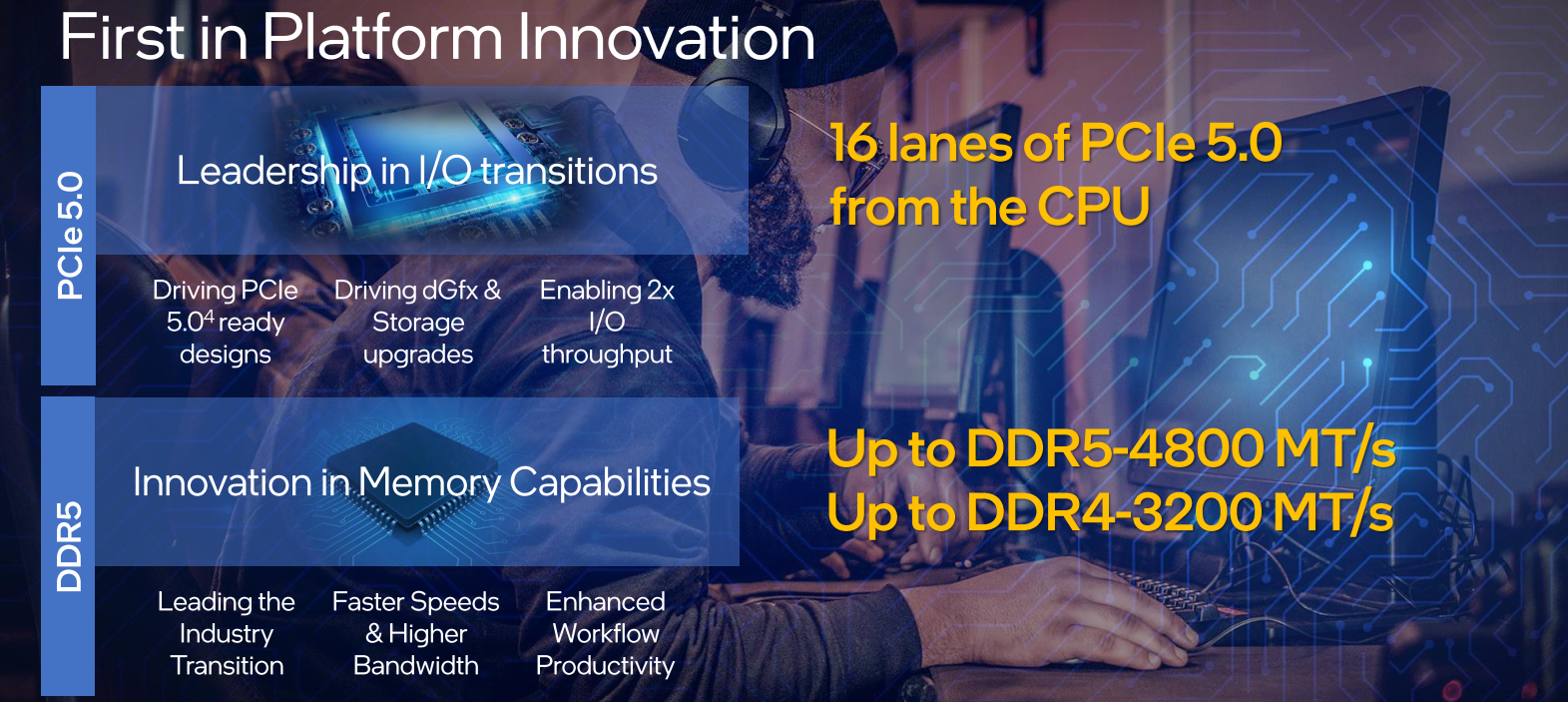
Beyond the core IP integration, Alder Lake introduces a number of fairly significant upgrades on the I/O front. All the new processors introduced today offer 16 lanes of PCIe 5.0. The memory subsystem was also upgraded to DDR5. Data rates of up to 4800 MT/s on DDR5 modules are supported. DDR4 is still supported as well to ease migration with rates up to 3200 MT/s.
600 Series Chipset
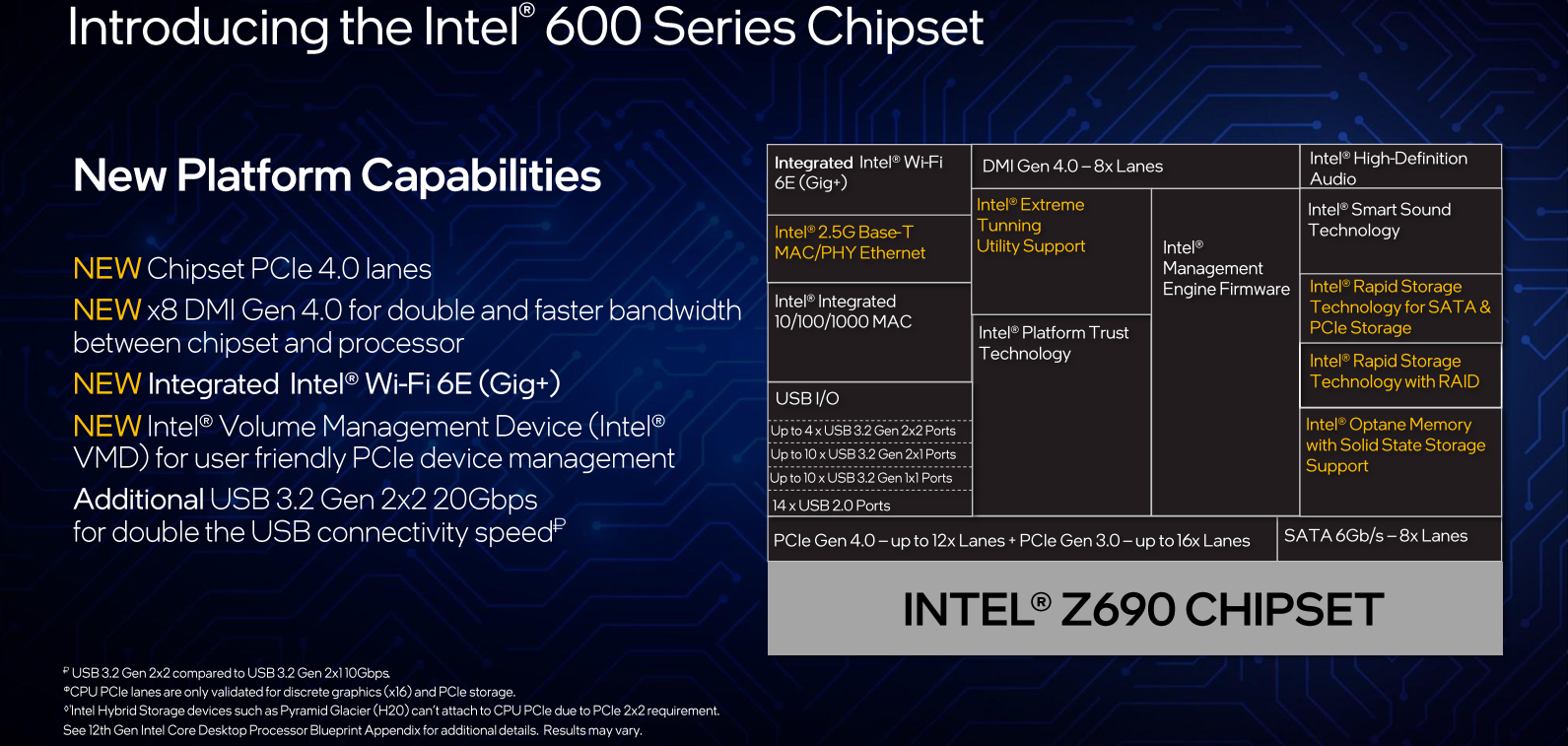
12th Gen Core processors go along with the new 600 Series Chipsets. Intel says that new chipsets have been upgraded to utilize PCIe Gen 4 as the underlying interconnect for their Direct Media Interface (DMI) 4.0, doubling the effective bandwidth. Additionally, the PCIe lanes offered by the chipset will now also be PCIe 4.0. A key technology feature offered by the new chipset is Volume Management Device (VMD), a feature originally limited to data center processors only but is now offered in the PC segment as well.
TDP PBP
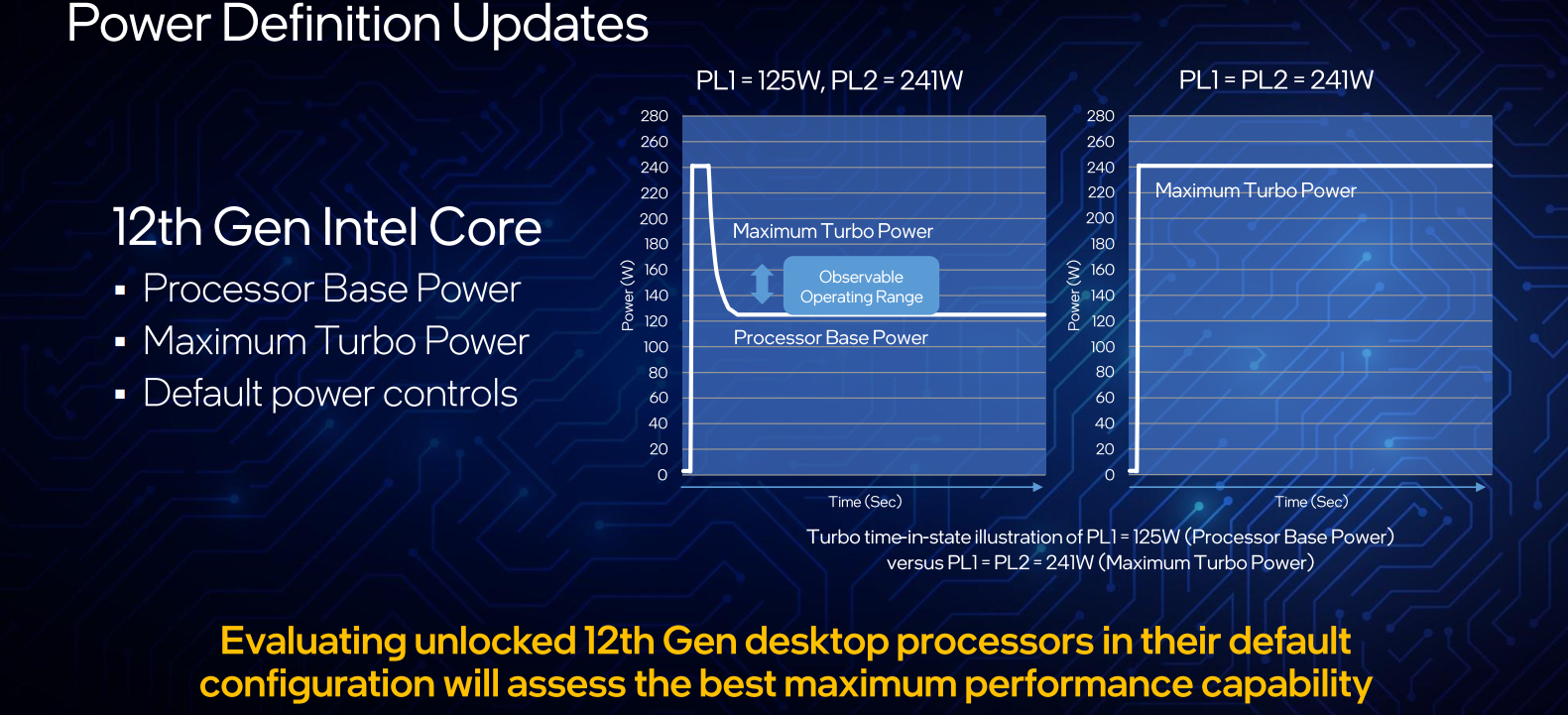
While the definition itself is not changing, instead of the usual thermal design point (TDP) terminology, Intel has decided to rename it Processor Base Power (PBP). Along with the Processor Base Power, Intel says it will also convey the chip’s Maximum Turbo Power which historically has been referred to as the PL2 value. On the new 12th generation K SKUs, Intel changed the default silicon power controls to allow sustained operation at Maximum Turbo Power. In other words, on the new 12th gen K SKUs, the turbo can be maintained indefinitely at the PL2 value (as shown on the graph on the right in the slide below).
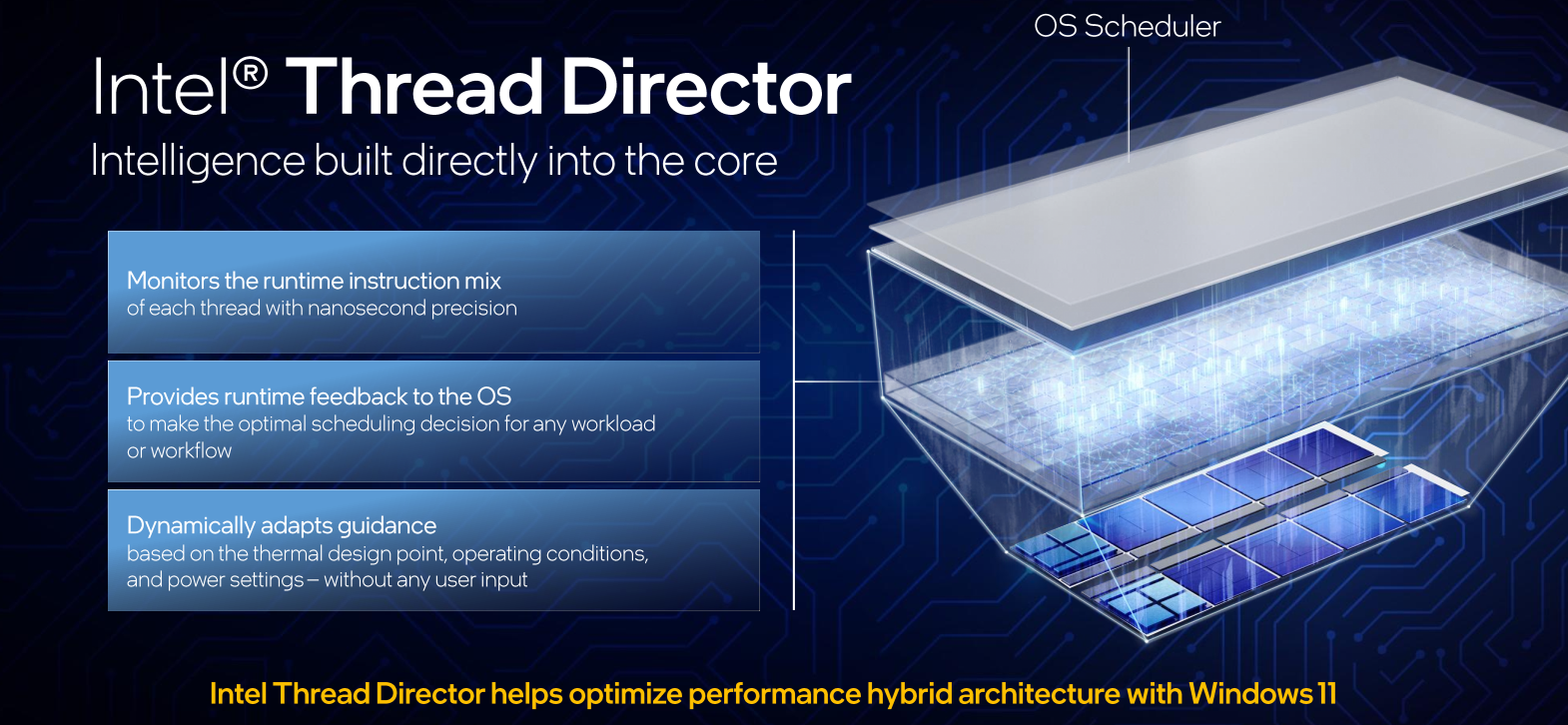
Thread Director
The success of Intel’s heterogeneous core integration hinges on the success of the new Thread Director Technology. Thread Director Technology is a hardware-based mechanism that uses real-time power and performance telemetry heuristics to determine the most appropriate thread placement across the P-cores and E-cores. Those hardware recommendations are sent directly to the OS scheduler to continuously orchestrate thread assignments in order to maximize performance and power.
Overclocking Enhancements
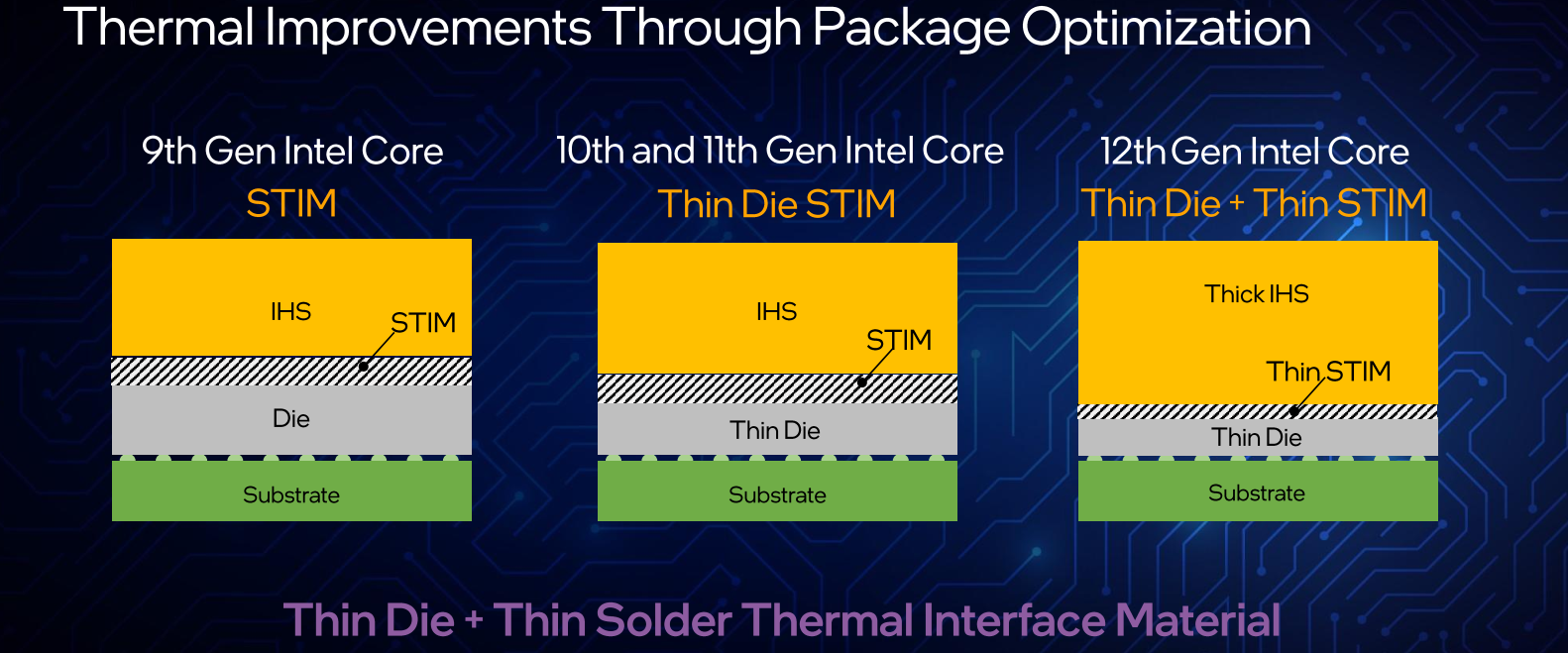
Die+STIM
In an effort to enhance the overclocking capabilities of the new processors, Intel introduced a number of new changes. One such change is the solder thermal interface material (STIM). Intel says it has thinned down the new processor dies by 25% and they’ve thinned down the STIM by 15% as well. The integrated heat sink (IHS) was made a bit thicker. The changes are said to improve the thermal transfer capabilities of the new processors.
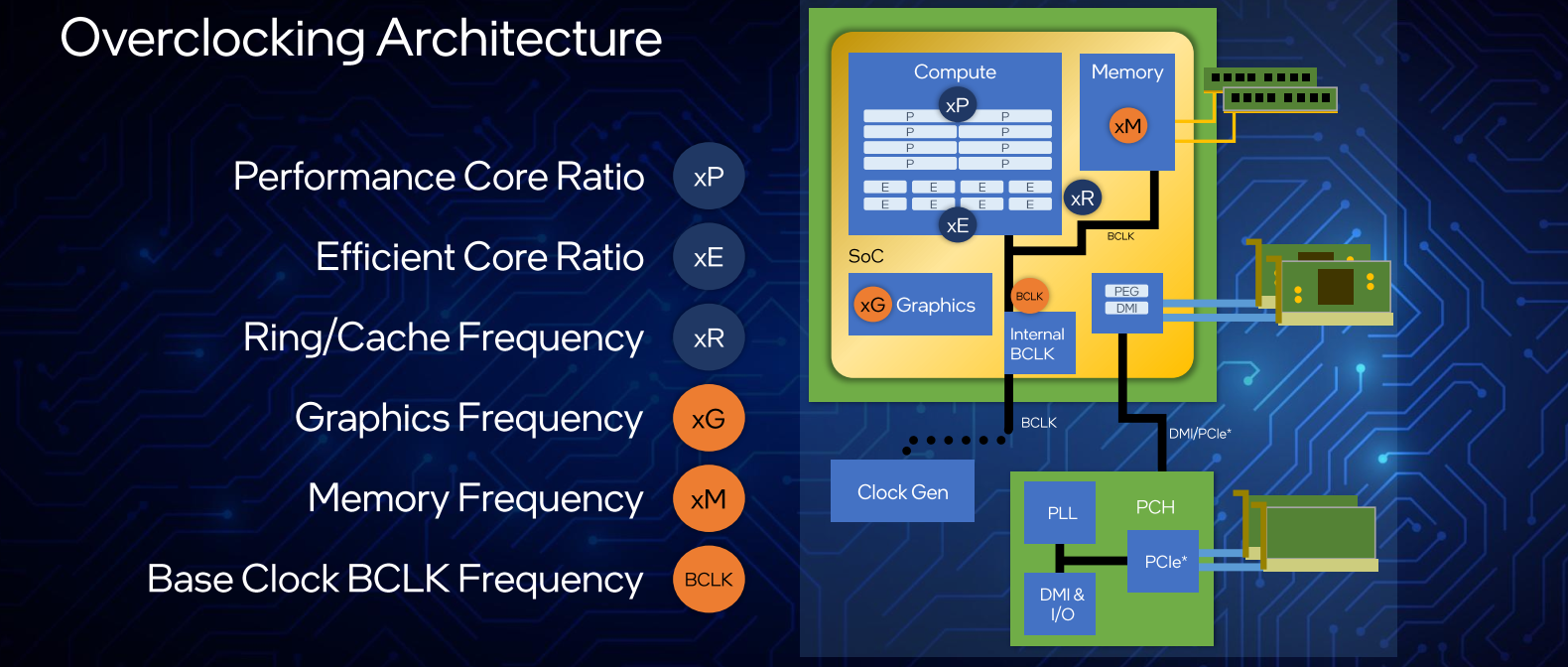
Ratio Controls
As with the prior generation, Intel offers various ratio settings for overclocks. With the introduction of the efficient cores on Alder Lake, Intel added a new efficient core ratio control knob for overclockers. Those cores are controlled in whole clusters. In other words, a ratio affects a group of four efficient cores at once. So for example, on the Core i9 processors with eight E-cores, it’s possible to control each of the two clusters individually.
Alder Lake offers various control knobs for overclockers. Those are summarized below. Some highlights include the ability to disable/enable individual cores as well as individual per-core multithreading support. The usual AVX offset, per-core Ratio and voltage controls are also present. BCLK-aware adaptive voltage-frequency curve allows the processor to automatically tune the voltage as necessary.
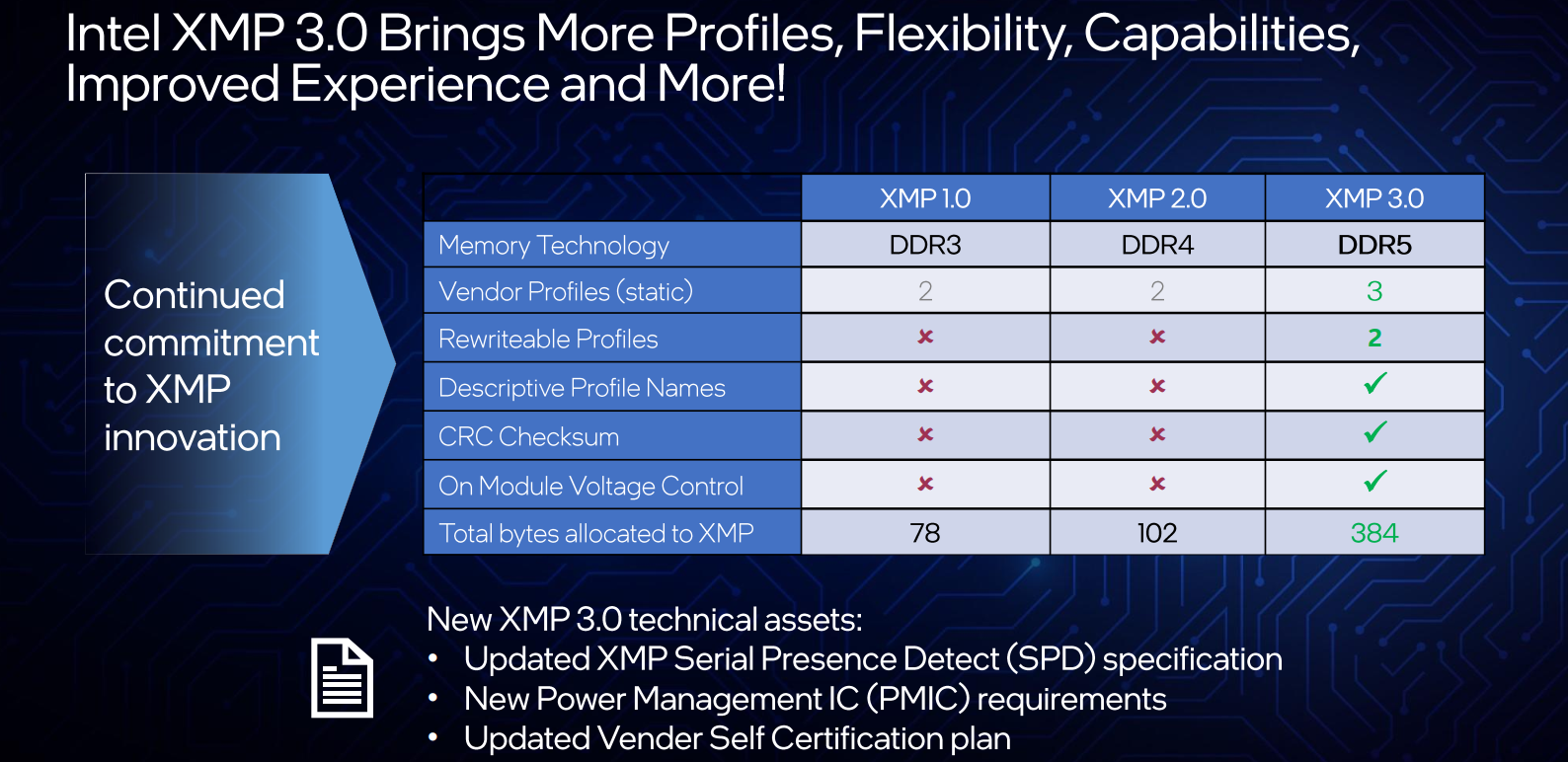
XMP 3.0
With today’s launch, Intel is also introducing XMP 3.0. Intel says six vendors have signed up and will offer XMP 3.0-supported memory (Crucial, GSkill, Corsair, Kingston, Patriot, and T-Force) with additional vendors being underway. The new version is said to offer more profiles – up to five (from two). This includes three vendor profiles and two rewritable profiles (can be set by the vendor or overwritten by the user). Profiles can now have descriptive names with up to sixteen characters. The new DDR5 modules introduce on-module local voltage regulation through the use of a power management integrated circuit or PMIC. With the new PMIC, DDR5 DIMMs offer new voltage configurability and monitoring features. XMP takes advantage of this and standardized the way voltages are controlled. There is also a new sandbox software feature that allows vendors to offer various configurations that can, in turn, be adjusted by the user and written back into one of the two rewritable profiles.
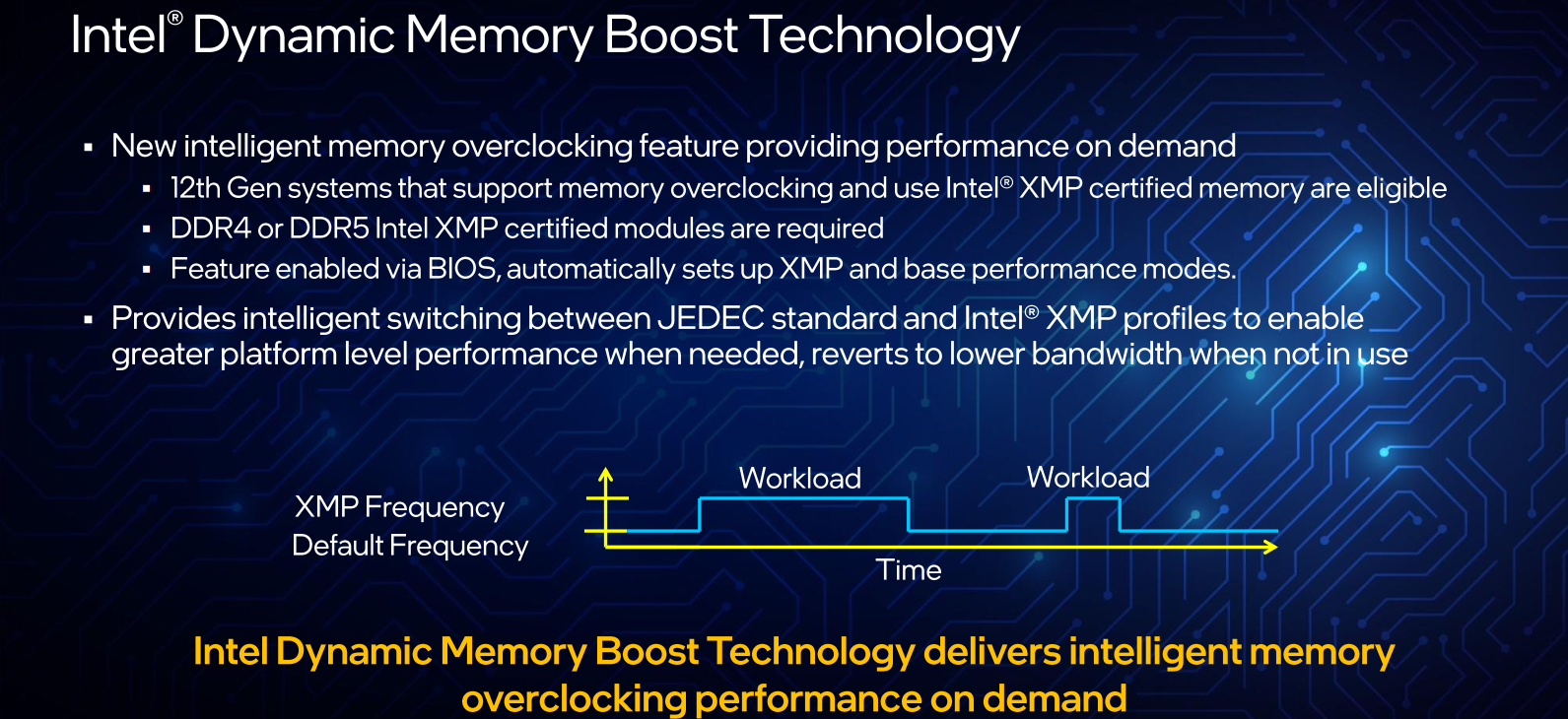
Dynamic Memory Boost Technology
One additional overclocking feature being introduced is Intel Dynamic Memory Boost Technology. This is essentially the turbo boost equivalent for memory. This mechanism builds on the 11th Gen real-time memory overclocking feature by making the overclocking frequency the new opportunistically turbo frequency. In other words, instead of manually enabling/disabling a fixed overclocking frequency for the memory, the new feature can autonomously automatically transition on-demand between the default frequency and the overclocked frequency.
Availability
Despite the tight supply chain, Intel says it is shipping 12th Gen Intel Core processors around the world to customers today. The company says it is working hard to ensure customers can find those products in store this year. Intel expects to ship hundreds of thousands of 12th Gen K-SKU processors in Q4 of this year with a record quarter for total K SKUs shipped ever. The company says it expects more than two million K-SKU units shipped by the end of Q1 2022.
The entire lineup announced today is now available for pre-order from participating OEMs, channel partners, and retailers. Broad availability will start on November 4.
–
Spotted an error? Help us fix it! Simply select the problematic text and press Ctrl+Enter to notify us.
–